Author: Tom Yin, Managing Partner at TJTC LLC
In today’s digital landscape, a multi-cloud and edge strategy is essential for data-intensive AI applications. However, organizations often face the immense challenge of managing network complexity and the steep costs of proprietary cloud routers, which can easily exceed thousands of dollars per month.
At a recent Linux Foundation event, a global team of open source experts presented a powerful, automated blueprint for seamless multicloud connectivity. Their solution proves that by combining the power of OpenStack and SONiC (Software for Open Networking in the Cloud), organizations can build a high-performance, agile network fabric at a fraction of the cost.
Driving Down the Unit of Economy with Open Source
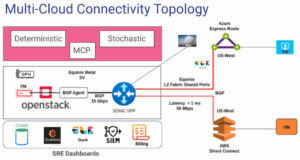
The core of this architecture’s economic advantage lies in its use of open source software on commodity bare metal hardware. Instead of paying for expensive managed Layer 3 cloud routers, this model leverages SONiC-VPP (Vector Packet Processing) on an Equinix C3 Medium Bare Metal Server to act as the central interconnection hub.
Here’s why this approach provides a lower unit of economy:
- Disaggregation: This model separates the network operating system (SONiC) from the physical hardware, eliminating vendor lock-in and allowing organizations to use cost-effective bare metal servers as their core routers.
- Reduced Overhead: By using SONiC-VPP on bare metal, this architecture delivered significant savings, proving to be up to 27% more cost-effective than a traditional managed cloud router solution.
- High Performance: This solution demonstrated the ability to transfer a petabyte of data in under 48 hours and successfully achieved a throughput of approximately 50 Gbps, matching the test environment’s interface bandwidth.
At the edge, the solution uses OpenStack on an Equinix Bare Metal Server to handle the creation and management of virtual machines. This combination of OpenStack for edge compute and SONiC for network routing creates a proven, open source blueprint for a secure and scalable solution.
The demo build provides the foundation to integrate with AI workloads and managing your infrastructure using trusted enterprise tools via SRE Dashboards. Here’s an example on how SONIC with OpenStack can integrate with enterprise tools to drive AI workloads.
AI Agility Through the Multi Context Protocol (MCP)
For AI workloads, not all traffic is created equal. A model training job requires massive data throughput, while a real-time inference task demands the lowest possible latency. Managing these distinct requirements, or “contexts,” across a hybrid environment is a major challenge.
This is where the Multi Context Protocol (MCP) integrates with the OpenStack/SONiC architecture to provide dynamic control. MCP functions as a signaling layer, allowing an AI orchestration platform to declare the specific needs of a workload to the network.
Here is how this synergy creates an intelligent, self-adapting network for AI:
- Context Declaration: An AI application can send an MCP request to the network orchestrator, such as: context=low_latency_inference, source=azure_vm, destination=edge_openstack_vm.
- Automated Enforcement: The orchestration layer interprets this MCP directive and triggers the architecture’s built-in automation tools—Terraform and Ansible.
- Dynamic Reconfiguration: These scripts then automatically reconfigure the network fabric to match the requested context. For a low-latency request, they would instantly optimize the BGP routing between Azure ExpressRoute, the central SONiC VPP hub, and the OpenStack BGP Agent to ensure the most direct path, achieving the sub-1 millisecond latency demonstrated in the project’s topology.
Because the automation enables network services to be deployed and torn down in minutes, the entire infrastructure can adapt on the fly. An MCP directive can change a connection from “high-throughput” to “low-latency” as an AI workload moves from its training phase to its deployment phase, ensuring resources are always perfectly aligned with business needs. X86-based SONIC-VPP switches accelerate enterprise data staging and rule-based labeling, streamlining conversion to .pt, TFRecords, and Parquet for AI training pipelines.
By combining an open source, cost-effective foundation with the intelligent signaling of a protocol like MCP, this OpenStack and SONiC architecture delivers the profound agility and control necessary to power the next generation of AI and edge computing, extending out to the galaxy.
To learn more about this project and its components, check out the reference links for Terraform, SONiC VPP, and the SONiC Automation scripts.
This blog was contributed by TJTC LLC, a community member demonstrating real-world SONiC deployment strategies. Contact tjtcllc@gmail.com for technical collaboration inquiries.